 Learning is a complex chemical dance. It requires the interaction of different cognitive processes, reactions across various neural pathways and numerous feedback loops. A key player in this chemical shuffle is dopamine.
Learning is a complex chemical dance. It requires the interaction of different cognitive processes, reactions across various neural pathways and numerous feedback loops. A key player in this chemical shuffle is dopamine.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a pivotal role in our reward system. But what impact does it have on a typical learning process?
Our understanding of the neuroscience of learning is constantly evolving. This is driven by advances in technology, innovation in teaching and new research.
As we build our understanding, we’ll be in a better position to optimise the learning experiences we provide across a variety of audiences. Ultimately, this will lead to better educational and business outcomes.
As we’ll see, dopamine plays its part in numerous physical functions and activities. It’s involved in learning, motivation, attention, memory and curiousity. It likes to keep busy! Understanding its role may change your approach to learning strategy.
Want a better understanding of how we learn, grow and thrive? Then read on.
What is Dopamine?
Dopamine was first discovered by the pharmacologist Arvid Carlsson, back in 1957. But what exactly is it?
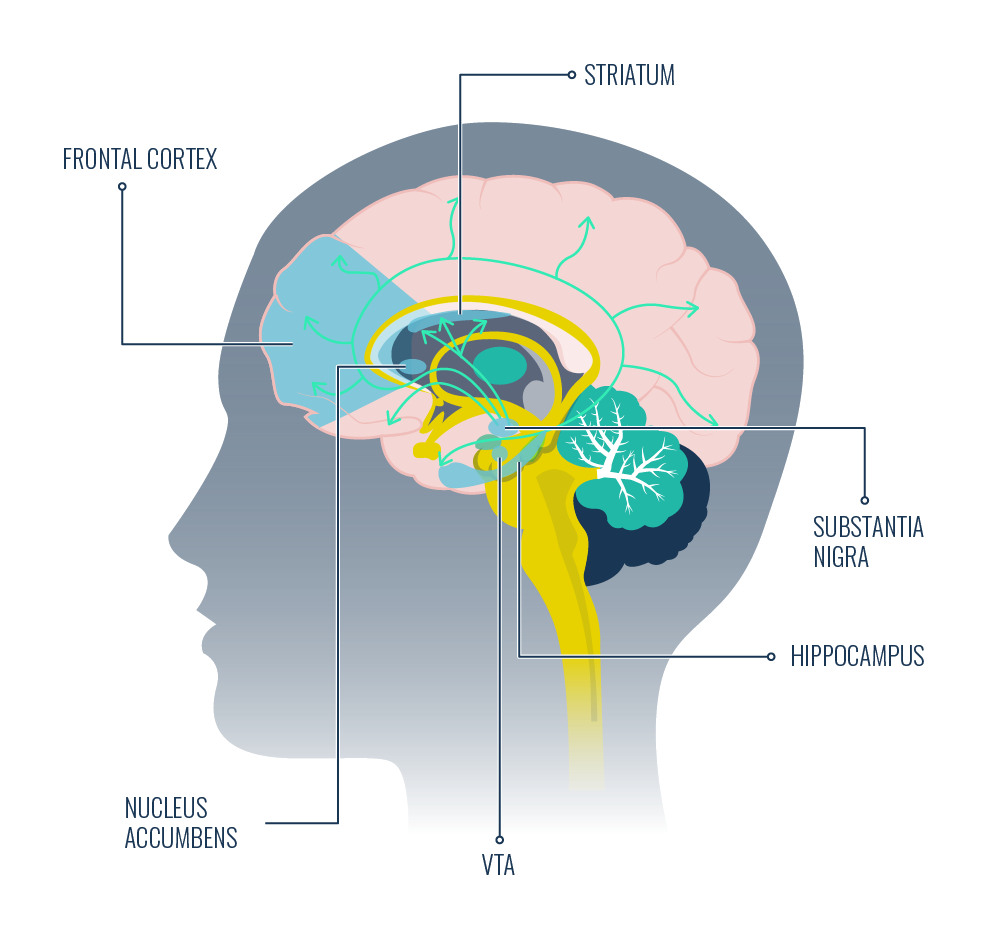
Put simply, dopamine is a neurotransmitter or chemical messenger. It’s produced by your body in the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area of the brain. Your nervous system uses it to send messages between nerve cells.
Dopamine’s role in the brain is complex and multifaceted. However, there’s a reason why it’s known as the ‘feel-good hormone’ (or the ‘Kim Kardashian of neurotransmitters’, as The Guardian dubbed it). When dopamine is released into your bloodstream, it gives you a sense of pleasure.
This in turn, forms a happy association between the pleasurable sensation and the associated act. As such, dopamine plays a key role in your reward system and motivation.
Sex, shopping and sugary treats are all pleasurable, in part, because they trigger a dopamine release. This leads us to enjoy them in the moment and crave them again in the future. This makes dopamine a powerful behavioural reinforcer.
After all, we are wired to seek out dopamine-induced pleasure. In fact, this pleasure serves an evolutionary purpose by guiding us to eat, drink, outcompete others and reproduce.
That said, there is a dark side to dopamine that’s worth mentioning. A repeated surge in dopamine levels can lead to dependency or addiction issues.
As Stanford psychiatrist, Dr. Anna Lembke puts it: our brains haven’t evolved for the “fire hose of dopamine” that comes with sex, drugs and other stimuli. Success lies in moderation and not sinking in the modern world’s dopamine deluge.
What Does Dopamine Affect?
As we’ve seen, dopamine plays a key role in your reward system. Specifically, however, it affects numerous physical functions and behavioural outputs. For instance:
- Learning (that’s what we’ll focus on in this article)
- Motivation
- Mood
- Attention
- Movement
- Sleep
- Pain processing
It’s even been shown to play a role in regulating your heart rate, blood vessel function, insulin production, nausea control, lactation and so on.
Dopamine & Learning: The Research
 As we know, dopamine is a neurotransmitter that helps to control reward-motivated behaviour. These are the activities we perform not just for their own sake, but in anticipation of an expected reward.
As we know, dopamine is a neurotransmitter that helps to control reward-motivated behaviour. These are the activities we perform not just for their own sake, but in anticipation of an expected reward.
These rewards strengthen our motivation to repeat the activity or behaviour. This positive reinforcement creates an addictive loop. Imagine if you could pull this off when it comes to learning.
For this to work, learning would need to be associated with positive, dopamine triggering, outcomes. For instance, the feel-good feeling when you achieve a goal, solve a problem or pick up a new skill.
Likewise, social praise, recognition or virtual rewards could be used to trigger dopamine release and encourage learning activity.
In fact, a recent study from the Netherlands Institute of Neuroscience has shown that dopamine serves a dual purpose in a learning environment.
Firstly, dopamine is ‘a learning signal’. It’s released when something better than expected happens and suppressed if something worse happens. In this respect, dopamine plays a similar role to the bell in Pavlov’s dog experiment. It triggers a conditioned response.
But it also does more than this. According to the study, it doesn’t just trigger action, it sustains it. In other words, it holds its own motivational power.
As such, conversations about dopamine shouldn’t focus on pleasure alone. As psychologist John Salamone notes, ‘low levels of dopamine make people less likely to work for things… it has more to do with motivation and cost/benefit analysis than pleasure itself’.
Dopamine: Other Learning Benefits
We’ve seen that dopamine can be used to trigger learning and provide further motivation. But the fun doesn’t stop there. Here are three other benefits that dopamine can have during a learning process.
1. Improved Focus:
As this National Library of Medicine study shows us, dopamine also ‘transmits signals related to non-rewarding experiences such as alerting events’. In other words, when dopamine is released in the brain, it makes us more alert and attentive.
It’s easy to see the benefits this would bring in a learning context. Imagine what you could achieve with your training programmes if your learners were more attentive or focused.
2. Improved Memory:
What’s more, dopamine is linked to the brain’s working memory system. As such, it helps to maintain information for short periods and facilitate problem solving and basic memorisation.
Moreover, according to Nature Reviews Neuroscience, dopamine also has an important role to play in the ‘consolidation of memory’. This happens when information is moved from your short-term memory to your long-term memory.
3. Deeper Curiosity:
Dopamine also has a tangible relationship with our capacity for curiosity. Research shows that dopamine is ‘intricately linked’ to our brain’s curiosity state. Exploration, discovery and the unexpected can all trigger the release of dopamine.
That’s the reason why doing something for the second time often feels less satisfying. For instance, watching the same movie again and again may result in diminishing returns (unless it’s It’s a Wonderful Life).
As Stanford neuroscientist Dr Andrew Huberman puts it, ‘dopamine is the universal currency of foraging, seeking and wanting more’. Just as cars need fuel, our curiosity requires dopamine.
How to Trigger a Dopamine Boost
Learning is challenging. We all want to get ahead in life, but we also have to contend with an unending onslaught of distractions. It’s hard to find the motivation to open up an eLearning unit when you could check Instagram or YouTube instead.
In the next section, we’ll look at how you can create a learning environment filled with dopamine triggers. But first, let’s look at the healthy habits that you can adopt to naturally increase your dopamine levels.
This will help you to expand your capacity for achievement. Ultimately, this will lead to better learning experiences and better learning outcomes.
- Eat Your Protein: Studies show that increasing tyrosine can raise dopamine levels in your brain. This can be obtained from protein-rich foods. Eating food full of natural probiotics like yoghurt and sauerkraut can also help.
- Stay Active: Exercise does a great job of boosting your endorphin levels. This, in turn, has a knock on effect on your mood and may also release dopamine.
- Sleep Well: Research shows that lack of sleep can reduce dopamine levels in your brain. On the other hand, good sleep hygiene helps to regulate your dopamine levels, ensuring you feel alert at the right moments throughout your day.
- Listen to Music: The right music can have a relaxing or mood-boosting effect on us. This can boost dopamine levels in your brain. Ready to learn? Pop on some Motörhead or Chopin.
- Find Inner Peace: Research also shows that meditation can increase your dopamine levels. By practising mindfulness, you can foster resilience and lower your stress levels.
Enhancing Learning Through Dopamine
We’ve seen that dopamine boosts motivation, focus and memory. As such, it’s worth asking the question: how can we create a dopamine-rich learning environment? Luckily, there is no shortage of approaches for you to try.
Focus on Engagement: Design learning activities that are inherently enjoyable and interesting to your learners. Don’t be afraid to find a middle ground between entertainment and education. If you create fun-focused learning experiences then dopamine levels are sure to spike.
Get Your Head in the Game: One great way to boost engagement levels is to deploy gamification or learning games. Gamification uses mechanics like Badges, XP and Leaderboards to incentivise your learners into action. In other words, it gives you another opportunity to reward activity and trigger dopamine.
Challenge Your Learners: Don’t make your learning content too easy. After all, the greatest challenges tend to also be the most rewarding. Create challenges, quizzes or battles that test your learners’ knowledge. Where possible, combine this with gamification to maximise impact.
Personalise Your Learning: Don’t forget that you’re creating learning experiences for individuals with different learning preferences. Tailor your learning environment accordingly. Where possible, grant learners autonomy and let them select their learning pathways or topics of interest.
Tell a Compelling Story: A good narrative can be difficult to resist. Storytelling also helps to make complex concepts easier to understand and more memorable. Furthermore, an engaging narrative tends to trigger an emotional response. This often leads to a dopamine spike.
Provide Recognition & Feedback: Timely and constructive feedback is a key part of any learning process. It helps learners to know whether they are heading in the right direction. Furthermore, positive feedback and recognition can help to trigger dopamine release.
Facilitate Social Learning: Learning’s often better when we do it together. After all, collaboration can lead to social rewards, an increase in status and a real sense of accomplishment. Utilising social or collaborative learning experiences can help to make this happen.
Celebrate Achievements: Providing feedback is one thing. But publicly recognising and celebrating your learners’ achievements can help to supercharge dopamine levels. You can do this through awards, certificates, newsletter shout-outs or events.
All this may seem like a big ask. But it doesn’t have to be. If you focus on making learning experiences that are enjoyable, meaningful and rewarding then results will follow.
Much of this can also be achieved through learning technology. For instance, Growth Engineering LMS focuses on engaging your learners through gamification, social learning and epic meaning (the unfiltered power of purpose).
The Dark Side of Dopamine
 Dopamine can help learners to form healthy habits, but it also has a role to play in addiction. With this in mind, there are some ethical considerations for you to mull over.
Dopamine can help learners to form healthy habits, but it also has a role to play in addiction. With this in mind, there are some ethical considerations for you to mull over.
It’s important that you educate yourself about the role dopamine plays in our brain. Understanding how it works will help you to make more informed decisions and design better learning experiences for your audience.
Use great caution when it comes to dopamine-fuelled behaviour manipulation. Just consider the pushback against how the tech industry has wielded dopamine in its quest to capture consumers’ hearts and minds.
As the former Vice President of User Growth at Facebook, Chamath Palihapitiya, put it: ‘The short-term, dopamine-driven feedback loops that we have created are destroying how society works’. You only need to look at smartphone usage metrics for further evidence.
As a learning professional, you are seeking to help your learners better themselves, develop skills and access new opportunities. Dopamine can help to serve these virtuous goals, but should be used with care and moderation.
As such, always keep your learners’ mental and emotional well-being in mind when designing your learning experiences. Consider their work-life balance and resist using dopamine to push your learners beyond any reasonable limits.
Dopamine and Learning: Final Words
There we have it. Over the course of this article, we’ve seen that dopamine is so much more than a ‘pleasure molecule’. It’s a vital key to unlocking our full potential as learners.
As a neurotransmitter it plays an important role in learning, motivation, attention, memory and curiosity. By understanding the neuroscience here, we can enhance our learning experiences, foster intrinsic motivation and build thriving learning cultures.
We’ve also seen how you can create learning environments that frequently trigger the release of dopamine. We recommend focusing on engagement, gamification, social learning and personalisation if you want to see the best results.
If you can get it right, each learning experience you share will transform into a dopamine-filled adventure. Now that sounds like something we can get behind.
Thanks for reading! Hungry for more brain food? Download our bumper 50+ page Guide to The Science of Learner Engagement now!









